#include <sim.h>
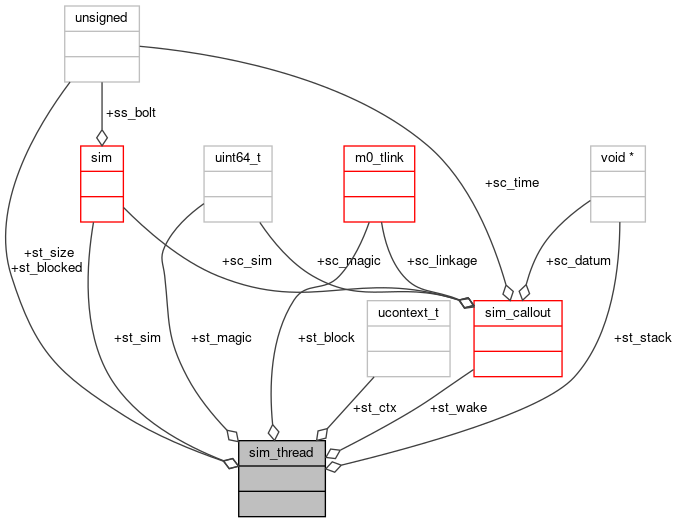
Data Fields | |
| struct sim * | st_sim |
| void * | st_stack |
| unsigned | st_size |
| ucontext_t | st_ctx |
| struct m0_tlink | st_block |
| sim_time_t | st_blocked |
| struct sim_callout | st_wake |
| uint64_t | st_magic |
Detailed Description
A thread in a simulated world.
Conceptually, a thread can always be replaced by a collection of call-outs. A thread is advantageous and natural to use when there is a lot of state to be maintained between call-outs and this state cannot be readily stored in some data-structure hanging off sim_callout::sc_datum. A thread uses native C language stack to store the state.
Threads interact with the simulation by sleeping (sim_sleep()), waiting on channels (struct sim_chan) and posting call-outs.
Current thread uses ucontext functions to implement lightweight and simple user-level threads. Blocking system call made from a sim_thread blocks the whole simulation.
With threads there are two modes in which simulation can be at the moment:
"thread mode", when one of the threads is running. In this mode the code is executed on the thread's stack; "scheduler mode", when no thread is running and simulation state is advanced by main simulation loop running on a stack where sim_run() was called, executing call-outs.
Note that this distinction is similar to "process" vs. "interrupt" modes of a traditional UNIX kernel.
A switch from thread to scheduler mode occurs when a thread is suspended (e.g., to wait on a channel) or exits. A switch in the opposite direction happens when a thread is resumed (e.g., woken up or starts for the first time).
Field Documentation
◆ st_block
| struct m0_tlink st_block |
linkage into a sim_chan::ch_threads list
◆ st_blocked
| sim_time_t st_blocked |
time when a thread was parked onto a channel. See sim_chan_wait() comments.
◆ st_ctx
| ucontext_t st_ctx |
◆ st_magic
◆ st_sim
| struct sim* st_sim |
◆ st_size
◆ st_stack
| void* st_stack |
allocated native stack, allocated in sim_thread_init()
◆ st_wake
| struct sim_callout st_wake |
pre-allocated callout to wake the thread. Used by sim_sleep() and sim_chan_{signal,broadcast}().
The documentation for this struct was generated from the following file:
- desim/sim.h
